The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed Incidence rate ratio = IRR = (854/100,000 PY) / (231/100,000 PY) = 854/231 = 37 Interpretation Women with BMI > 30 had 37 times the rate of having a nonfatal myocardial infarction compared to women with BMI < during the study period And Incidence rate difference = IRD = 854/100,/100,000 = 62/100,000 PY Interpretation Among the The Hazard ratio (HR) is one of the measures that in clinical research are most often difficult to interpret for students and researchers In this post we will try to explain this measure in terms of its practical use You should know what the Hazard Ratio is, but we will repeat it again Let's take as an example a study in which I want to evaluate the survival of patients exposed to

What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation- HOW TO INTERPRET A HAZARD RATIO As discussed earlier, a simplistic interpretation is that if the HR (E versus C) is 1 The following examples illustrate more detailed explanations and common pitfalls Appropriate Interpretation Suppose the HR (E versus C) =It is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratios
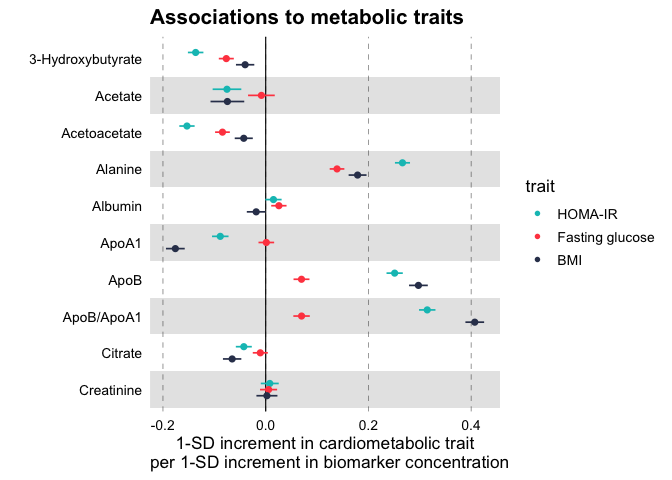



Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot
It's a ratio of events to nonevents You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2 Just like the risk ratio, it's a way of measuringLogistic regression log (odds) = The way to interpret the exposure coefficient, 1, in Cox regression is similar to the way you interpret the exposure coefficient in any log model It is the difference between the loghazard per one unit increment in E, which is equivalent to the log of the hazard ratio 1 = log (hazard ratio) Exponentiate the coefficient and you get the hazard ratio The interpretation of the hazard ratio is also similar to the rate ratio the hazard of a poor outcome in the group treated with aspirin and dipyramidole is 080 times the hazard in the group treated with aspirin alone, a relative reduction of % Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the odds of treatment (ie number of subjects with treatment divided by number of subjects without
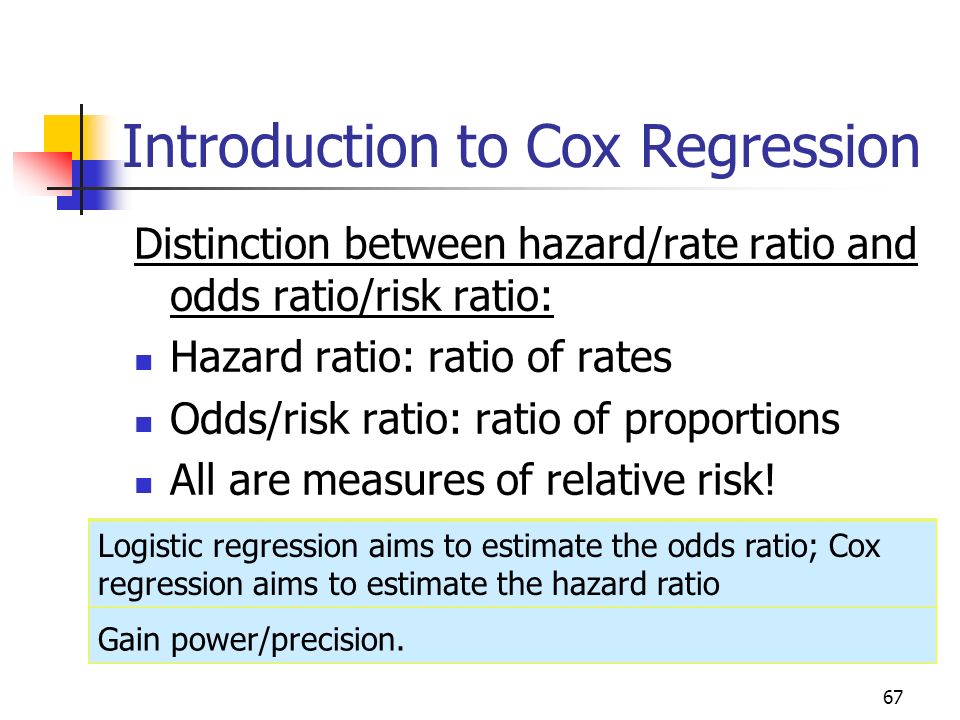
The hazard ratio for mortality from colorectal cancer, comparing intervention with control, was 073 (95% confidence interval 047 to 113) The hazard ratio was less than unity, indicating that the hazard of death in the screening group was less than that in the control group At any time during followup participants in the intervention groupCox regression vs logistic regression Distinction between hazard/rate ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper
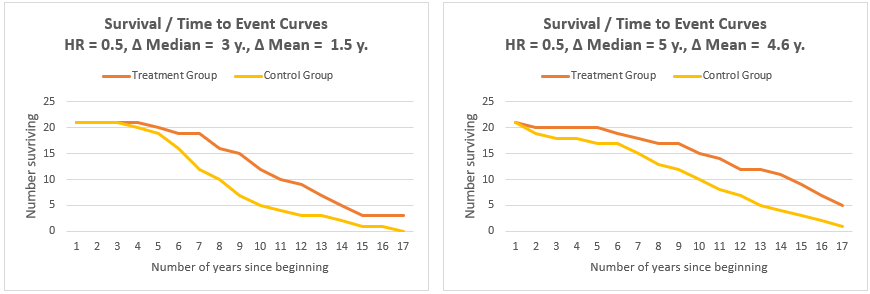
Nelsonlen cumulative hazard estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 100 0 300 400 group 0 group 1 Hazard Ratio = 71 KaplanMeier survival estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 025 050 075 100 group 0 group 1 Title Point Estimation Odds Ratios, Hazard Ratios/Rates, Risk Differences,Precision Author Garreel Created Date 6/6/08When hazard ratios are used in survival analysis, this may have nothing to do with dying or prolonging life, but reflects th This video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratios In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR Interpretation of Hazard Ratio Because Hazard Ratio is a ratio, then when HR = 05 at any particular time, half as many patients in the treatment group are experiencing an event compared to the control group HR = 1 at any particular time, event rates are the same in both groups, HR = 2 at any particular time, twice as many patients in the treatment group are




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Number Needed To Treat
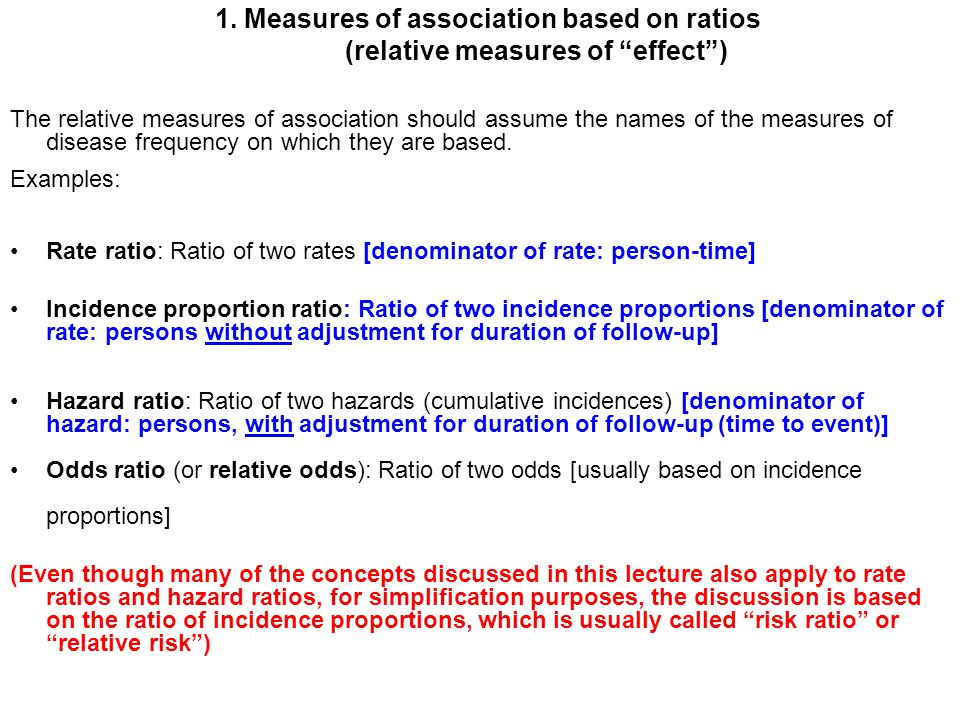
The hazard ratio, sometimes called a relative hazard, is typically used to compare time to event data between two treatment groups The hazard ratio of death for the intervention group compared with the control group was 046 (022 to 095) The hazard ratio was derived as the ratio of the hazard of death for the intervention group to the hazard of death for theThis is called the odds ratio; Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
Essentially, the odds ratio estimate the _______ in these types of studies Risk ratio What is the definition of odds ratio? Here is how to interpret the results Age The adjusted odds ratio for age is calculated as e045 = 1046 This means the odds of having a baby with low birthweight are increased by 46% for each additional yearly increase in age, assuming the variable smoking is held constant For example, suppose mother A and mother B are both smokers If mother A is oneThe odds ratio is used when one of two possible events or outcomes are measured, and there is a supposed causative factor The odds ratio is a versatile and robust statistic For example, it can calculate the odds of an event happening given a particular treatment intervention (1) It can calculate the odds of a health outcome given exposure




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
Relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided, wherever necessary J Clin Psychiatry 15;76(7)e857A logrank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing timetoevent data gives rise to something in between The appropriate effect measure should be specified in RevMan Only fixedeffect metaanalysis methods are available in RevMan for 'O – E and Odds = P (positive) / 1 – P (positive) = (42/90) / 1 (42/90) = (42/90) / (48/90) = 0875 Thus, the odds ratio for experiencing a positive outcome under the new treatment compared to the existing treatment can be calculated as Odds Ratio = 125 / 0875 = 1428 We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a patient experiences a



Hazard Ratio



Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
Peto's method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9442) gives rise to an odds ratio;The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simple event rate in a group of people who receive an intervention (see Example 1)Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times The term is typically used in the context of survival




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR willOdds ratios, like odds, are more difficult to interpret (Sinclair 1994, Sackett 1996) Odds ratios describe the multiplication of the odds of the outcome that occur with use of the intervention To understand what an odds ratio means in terms of changes in numbers of events it is simplest to first convert it into a risk ratio, and then interpret the risk ratio in the context of a typicalOdds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure Important points about Odds ratio Calculated in casecontrol studies as the incidence of outcome is not known;




Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers



Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler
RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patWhile hazard ratios allow for hypothesis testing, they should be considered alongside other measures for interpretation of the treatment effect, eg the ratio of median times (median ratio) at which treatment and control group participants are at some endpoint If the analogy of a race is applied, the hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32 , 41 , 50 52




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Hazard And Hazard Ratio In Statistics
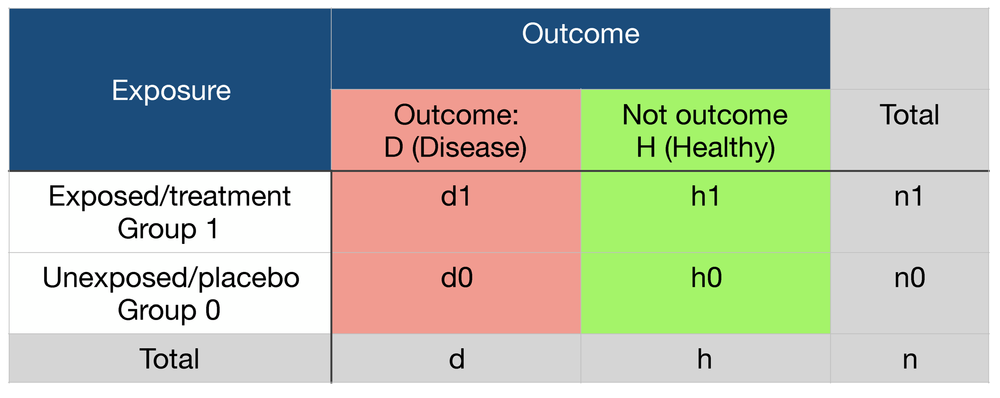
Risk (hazard) ratios and odds ratios cannot be used interchangeably in metaanalysis Like euro and pound they have to be converted into the same value eg Swedish crowns You find theOR >1 indicates increasedOdds that a person with an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed)/ Odds that a person without an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed) Odds group 1/odds group 2




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio
When events in the intervention group are significantly less frequent than in the control group, then relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will be greater than 10 Introduction In randomised trials and systematic reviews of trials, the effects of new treatments on dichotomousThanks and Regards Fred Jeremy Miles unread, Aug 25, Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;



1



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
It is a common practice when reporting results of cancer clinical trials to express survival benefit based on the hazard ratio (HR) from a survival analysis as a "reduction in the risk of death," by an amount equal to 100 × (1 − HR) % Stating, for instance, that "drug X reduces the risk of dying by 40%," based on an observed survival HR of 060, is a typical way ofRelative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?Interpretation of the Hazard Ratio Hazard ratios of interest are derived using the regression coefficient of the Cox model and can reflect comparison of two different sets of covariate values as shown previously or a single covariate If, for example, the covariate X i is status for a particular risk factor (0 for risk factor absent, 1 for risk factor present), then the hazard ratio is




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
Lead authors of studies reporting hazard ratio results were contacted to obtain raw data or alternative analysis results (eg, odds ratios) to allow all 11 studies to be analyzed together So, the rate ratio was 047 Interpretation Women who used postmenopausal hormones had 047 times the rate of coronary artery disease compared to women who did not use postmenopausal hormones (Rate ratios are often interpreted as if they were risk ratios, eg, postmenopausal women using HRT had 047 times the risk of CAD compared to women not usingAn odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor
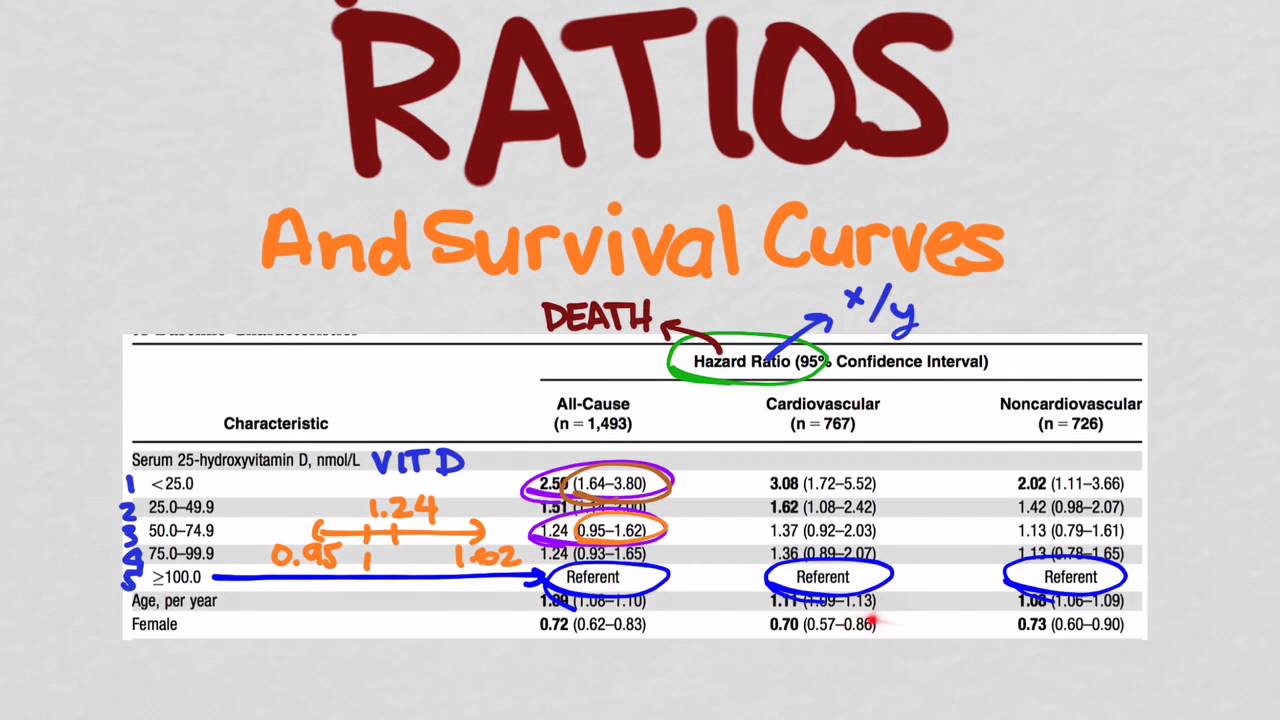



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science
This video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratiosOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR); The interpretation of a hazard ratio is essentially the same as an odds ratio However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratio
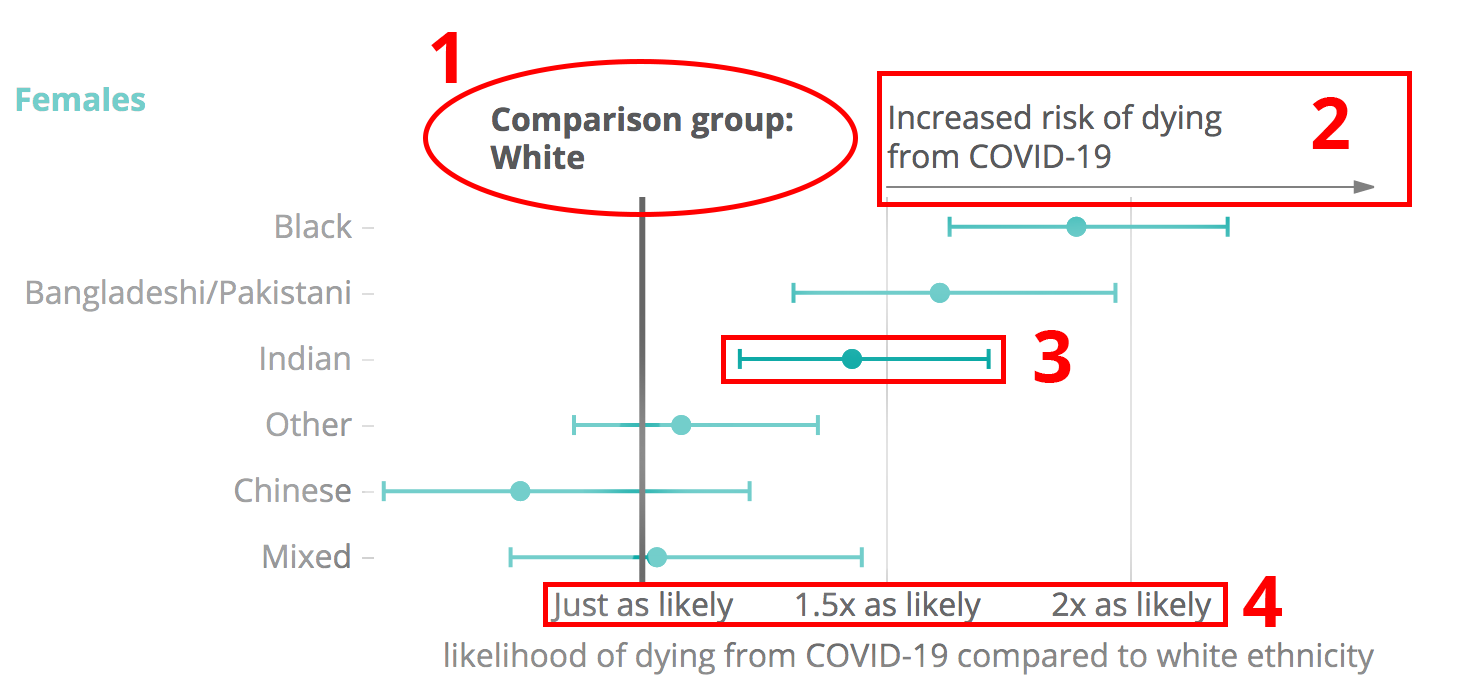



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
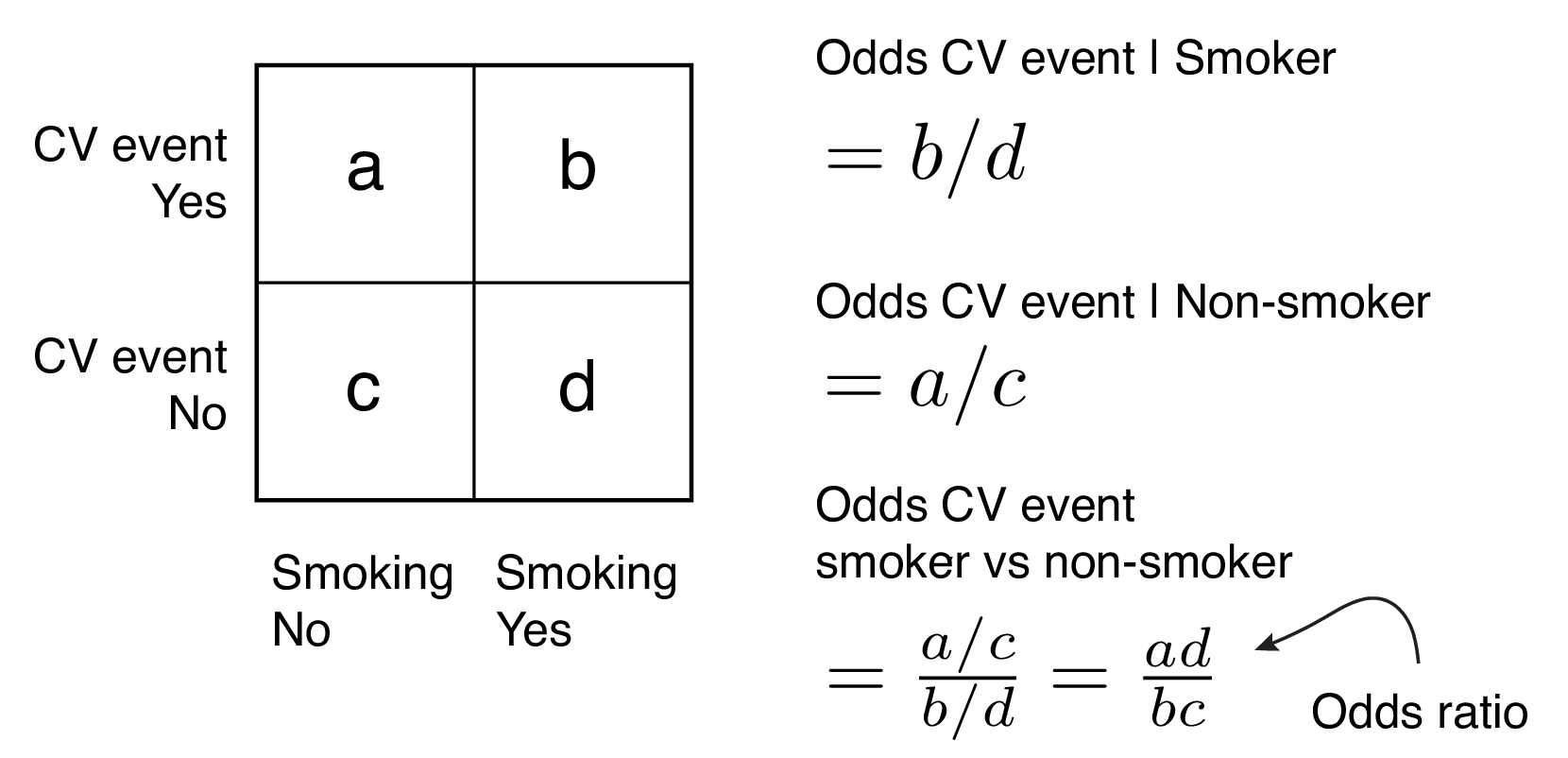



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
2 Specify the MetaAnalysis of Hazard Ratios procedure options • Find and open the MetaAnalysis of Hazard Ratios procedure using the menus or the Procedure Navigator • The settings for this example are listed below and are stored in the Example 1 settings template To load Introduction and background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratiosThe issue in experimental design is when a fixed endpoint (odds ratio) rather than a broader survival analysis (hazard ratio) is appropriate Typically, you use a fixed endpoint if almost everyone will get to that time point and you don't care about what happens thereafter Otherwise, survival analysis should be better




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
Effect size measures For studies that look at treatment effects or other effect sizes the program will compute the odds ratio, risk ratio, risk difference, standardized mean difference (d), biascorrected standardized mean difference (Hedges's g), raw mean difference, correlation, hazard ratio, rate ratio, and moreAs odds ratio and hazard ratio are the approximation to the relative risks, but they could be adjusted in multivariable settings When conducting a meta analysis, for the same disease and exposure, if publications report those three, also their adjusted values, then what we need in the final meta analysis?Entities based on odds and hazard ratios When events in the intervention group are significantly less frequent than in the control group, then relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will be greater than 10 Key words clinical trials, number needed to treat, odds, statistics (Aust Prescr




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



2



2




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



2




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
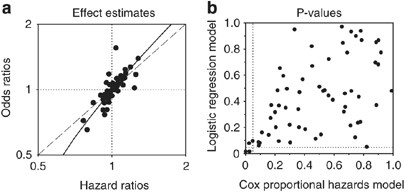



Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



Tests For Time To Event Outcomes Survival Analysis Ppt Download




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Article




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora




7 Stats Ideas Research Methods Statistics Math Nursing Research




Confidence Intervals And P Values




Forest Plot Wikipedia



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
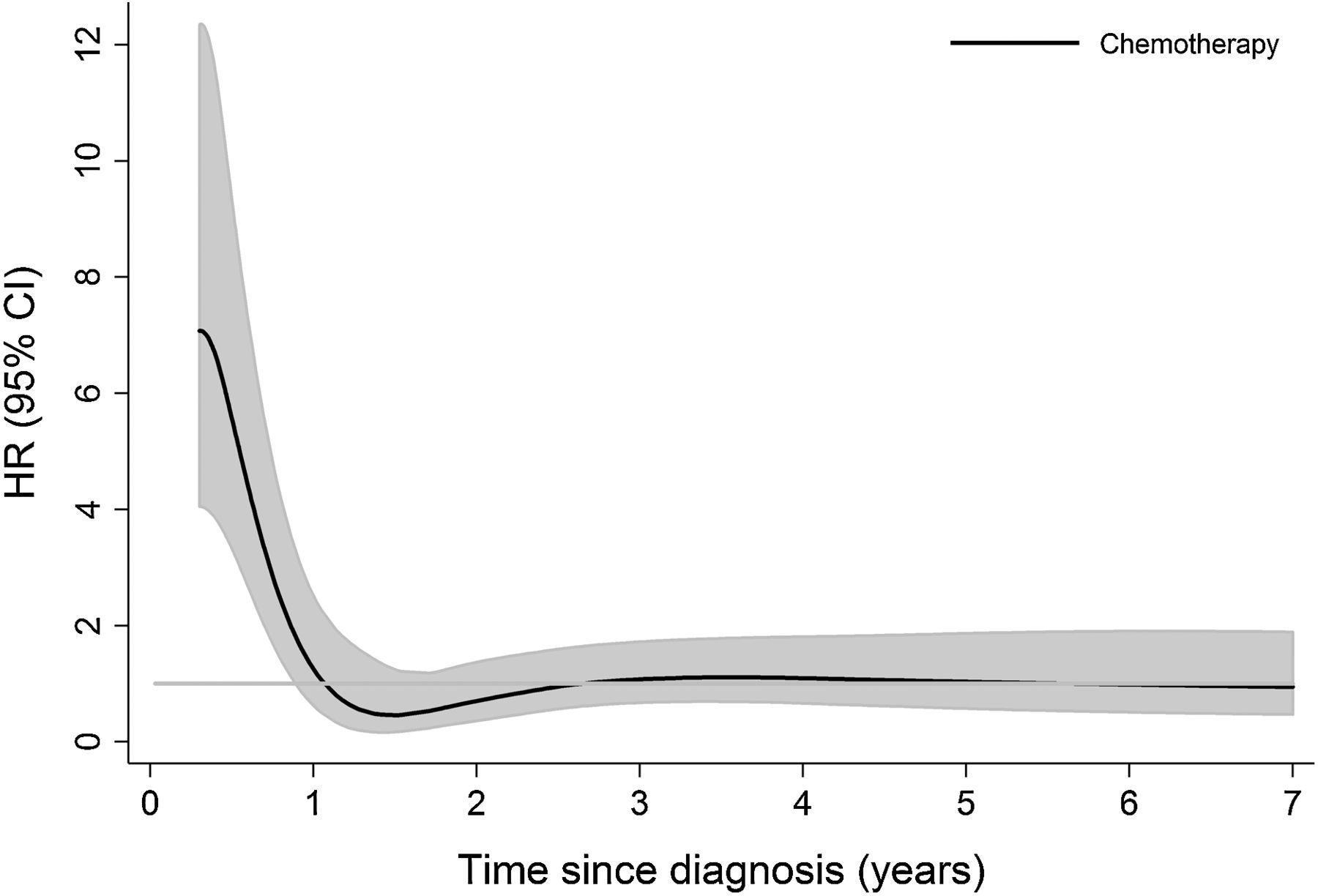



Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Logistic Regression And Survival Analysis




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
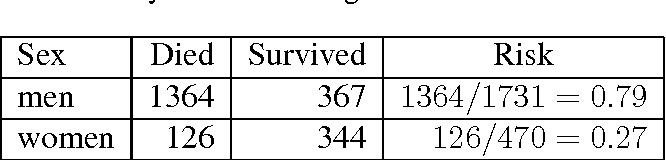



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
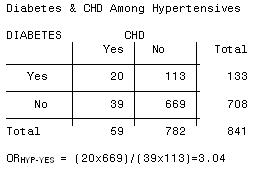



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
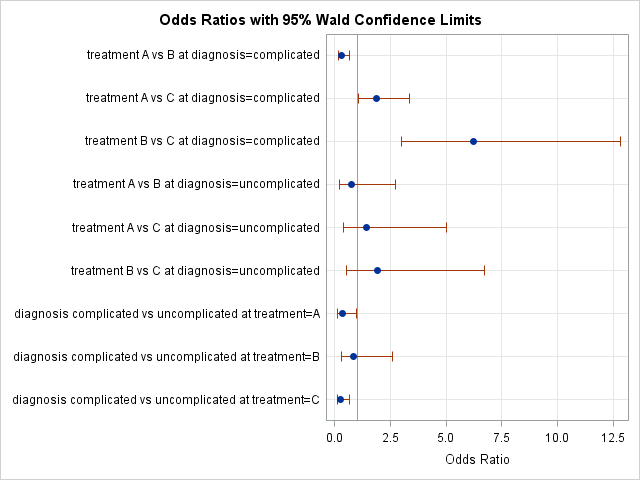



Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop




Relative Risk Wikipedia




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler
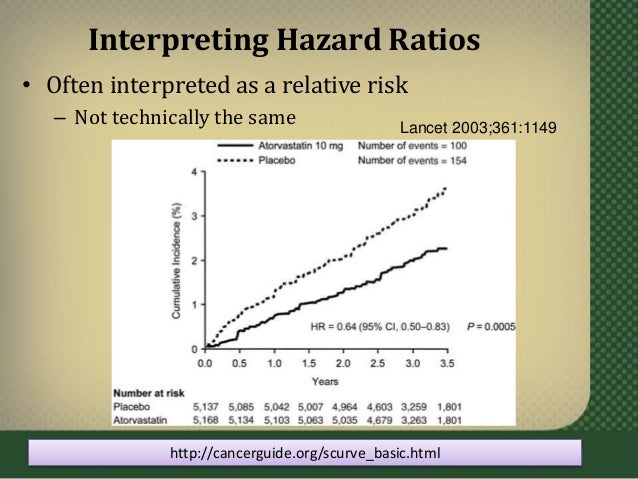



Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Wikipedia




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value




Statistics 103 Monday July 10 17 Survival Analysis
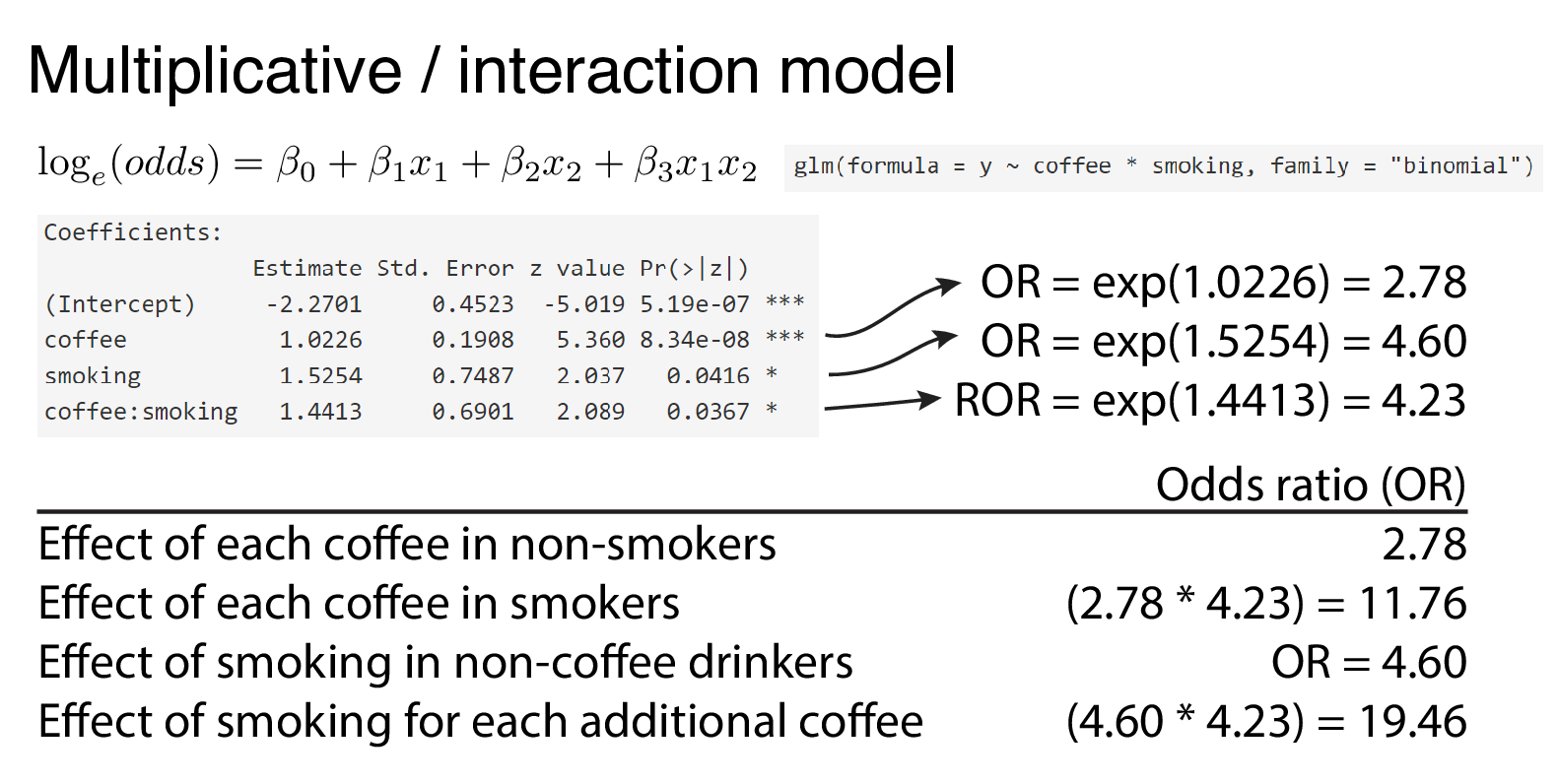



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
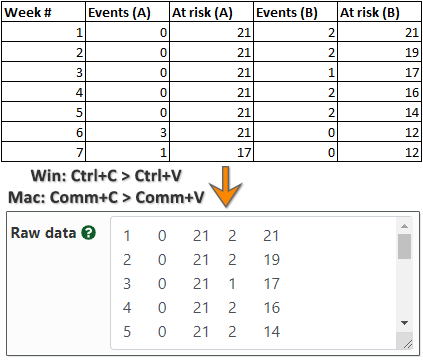



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Delta Method Standard Errors



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
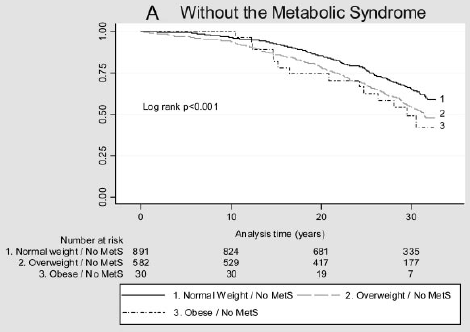



Lesson 13 Proportional Hazards Regression Stat 507




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



2




Introduction To Cox Regression Kristin Sainani Ph D



2




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



1




Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio




Interpretation Of The Hazard Ratio In A Spline Model On Continuous Exposures Cross Validated




A Forest Plot Showing The Hazard Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿